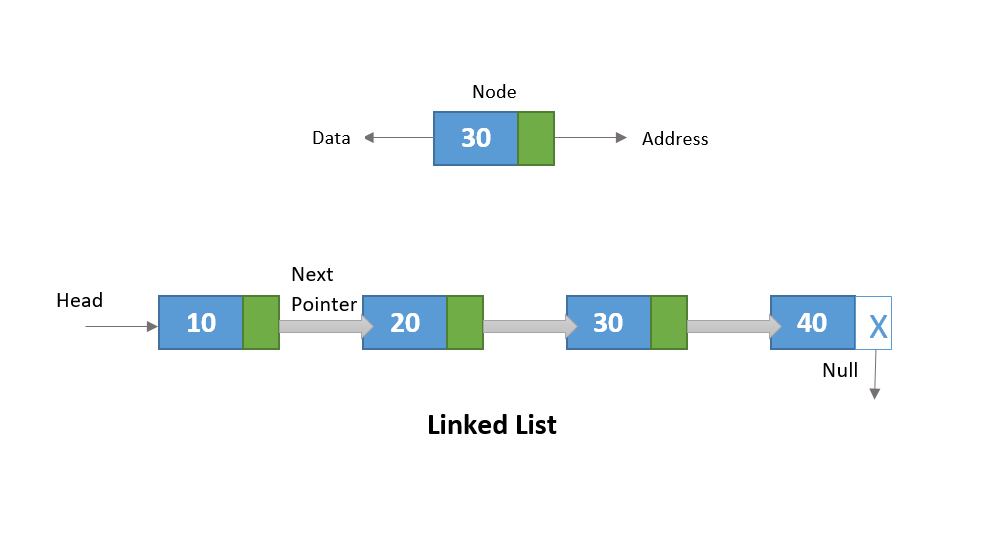
//****************************
//LinkedList.java
//****************************
// Modified to support backwards traversal of the list.
// Additions and modifications are marked by ***.
public class LinkedList {
private ListItem start; // First ListIem in the list.
private ListItem end; // Last ListIem in the list.
private ListItem current; // The current item for iterating.
// Constructor to create a list containing one object:
public LinkedList(Object item) {
start = new ListItem(item); // item is the start
current = end = start; // as well as the end and current.
}
// Construct a linked list from an array of objects:
public LinkedList(Object[] items) {
// Create a one item list:
start = new ListItem(items[0]); // First item is the start
end = start; // as well as the end.
// Now add the other items:
for (int i = 1; i < items.length; i++)
addItem(items[i]);
}
// Add an item object to the list:
public void addItem(Object item) {
ListItem newEnd = new ListItem(item); // Create a new ListItem.
end.setNext(newEnd); // Set next variable for old end as new end.
newEnd.setPrevious(end); // So previous for new item. ***
current = end = newEnd; // Store new item as end and current. ***
}
// Get the first object in the list:
public Object getFirst() {
current = start;
return start.getObject();
}
// Additional method to get the last object in the list: ***
public Object getLast() {
current = end;
return end.getObject();
}
// Get the next object in the list:
public Object getNext() {
current = current.getNext(); // Get the reference to the next item.
return current == null ? null : current.getObject();
}
// Additional method to get the previous object in the list: ***
public Object getPrevious() {
current = current.getPrevious(); // Get the reference to the previous item.
return current == null ? null : current.getObject();
}
}
//****************************
//ListItem.java
//****************************
// Modified to support backwards traversal of the list.
// Additions and modifications are marked by ***.
public class ListItem {
ListItem next; // Refers to next item in the list.
ListItem previous; // Refers to the previous item. ***
Object item; // The item for this ListItem.
// Constructor:
public ListItem(Object item) {
this.item = item; // Store the item.
next = previous = null; // Set next and previous to null. ***
}
// Set the pointer to the next ListItem:
public void setNext(ListItem next) {
this.next = next; // Store reference to the next item.
}
// Additional method to set the pointer to the previous ListItem: ***
public void setPrevious(ListItem previous) {
this.previous = previous; // Store reference to the previous item.
}
// Get the next item in the list:
public ListItem getNext() {
return next;
}
// Additional method to get the previous item in the list: ***
public ListItem getPrevious() {
return previous;
}
// Get the object for this item:
public Object getObject() {
return item;
}
// Return class name & object:
public String toString() {
return "ListItem " + item;
}
}
//****************************
//Point.java
//****************************
public class Point {
double x;
double y;
// Constructors:
public Point() {
x = 0.0;
y = 0.0;
}
// Construct a Point from its coordinates:
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
// Construct a Point from another Point:
public Point(Point point) {
x = point.x;
y = point.y;
}
}